The Wide View
Capturing And Printing Digital Panoramas
People have been fascinated with panoramic imagery ever since the beginning of photography, but my own fascination can be traced back to Bausch & Lomb's invention of CinemaScope lenses for the movies during the 1950s. The first CinemaScope movie, The Robe, had an original projected aspect ratio of 2.66:1, but over time this changed for various technical reasons, eventually evolving into the 2.35:1 that is commonly used today. While I saw the film in November, 1953, I remember little about the plot or even the stars; what I remember most was the wide screen and I've been in love with that view ever since. Capture The Image. For me, nothing captures scenic vistas like a panoramic photo and nothing can be more fun to print using the tools found in your digital darkroom. While purists might debate some of the specifics of panoramic photography that follow, I prefer working with the dictionary's definition of panorama that says that it's an "extended pictorial representation of a landscape or other scene." |
|||
|
|||
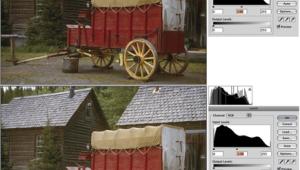
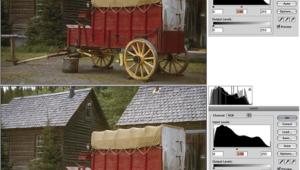
Stitching Digital Images. Many photographic companies sell panoramic adapters that can be attached to tripods, then after a cameras is mounted you can precisely photograph several sequential images using a film-based or digital camera. After the images are digitized, you can use software to stitch them together to form a continuous image. This is an especially useful technique when working with images captured from digital cameras because it effectively multiplies the resolution of the capture device, enabling it to create a higher resolution image than the camera is inherently capable of producing. Stand-alone stitching software is available from many companies including Enroute's QuickStitch and PowerStitch, Ulead Systems' Cool 360, and this feature is sometimes built into digital imaging programs such as ArcSoft's PhotoStudio 2000. Here's a look at how images can be combined into a stitched panorama using PhotoStudio 2000. Step 1: The original photographs were made using a Kodak DC290 Digital Camera using the highest quality compressed mode and saved as a JPEG file. The images were directly opened into PhotoStudio 2000 from a CompactFlash card using Microtech's USB Camera-Mate. Step 2: The Stitch command can be accessed through the Effects menu or a button on the toolbar. A Stitch Control Panel allows you to place the two image files on the left and right and specify how much blending (overlap) there will be between the two. It sounds complicated and with just a little practice, you'll see how easy it is. Step 3: Use the Stitch command to stitch the two images together creating a panoramic image. After the image is stitched, you will have to trim off any areas that were created when the two horizon lines of the images were blended. |
|||
Just because you don't have any panoramic images doesn't mean you can't create your own from scratch. The same technique that's used to create real panoramas can be used to create faux images made from a single original photograph. In Arcsoft's PhotoStudio 2000 you can use the Mirror option in the Rotate window to create a mirror image of your original image, then after saving it under a different name, you can stitch the two together to produce what I call a faux panorama. Printing Panoramas. Panoramic images are often printed very large--even from these small originals--so additional care is required in preparing panoramic images for output. Thanks to the panoramic options of 35mm and APS cameras, prints of panoramic images have become ubiquitous enough that every Wal-Mart store seems to have desktop frames that hold these long, skinny prints. When making desktop panoramic prints using standard ink jet papers, no radically different techniques are required, but there are a few points to keep in mind when working with photographs such as APS, 35mm panoramic, or similar images that are carved from larger images. While working with any digital image, it's a good idea to be concerned about all of these items, they are especially important when working with small-sized originals, and only slightly less important when working with images made with real panoramic cameras where you will be using 100 percent of the digitized original negative or transparency. Specialty Papers. While you can print panoramic images on any sheet of paper, it's going to be less wasteful to use long, skinny sheets that have already been prepared for panorama printing. Epson makes a Panoramic Photo Paper (SO41145) that measures 8.3x23.4" and is available in 10-sheet packs and will work with any brand of ink jet printer. When working with special sized papers, you will need to set your printer driver to accept it. Epson printers have a built-in setting for panoramic paper, but printers from other companies will surely not. One way to get around this limitation with printers lacking this setting is to print your image using a desktop publishing program, such as Adobe PageMaker, instead of an image-editing program. PageMaker's Document Setup function can be used to tell the printer that the output would be a "custom" print made on a non-standard paper size. Not all printers will cover completely from one edge of the paper to the other. The best way to find out how much area you can really print is to make a test print. Start by using a graphics program to draw a rectangle that can be filled with color. Don't use rich solid colors. To save ink, use soft colors. If your driver provides a choice of printing in less than high-quality modes do that, too. You only need to see how much area is being covered; so why waste any ink to uncover this information. Unlike a test file that's used to evaluate the printer's photo quality output, be sure to use the least expensive paper you have for this test. After you print the test file, evaluate the results to see how close to the edge you can really come. Don't be discouraged to find that your printer will not cover the entire page. Most printers need some space for paper handling and this shows up in what areas are covered by ink. This information will let you know what kind of border to provide when printing images on panoramic and other kinds of special papers. As an alternative to using specialized panoramic papers, you can use roll paper, much the same way that professional photo labs produce wide prints or a series of standard-sized silver-based photographs. As I write this only Epson offers paper for ink jet printers in rolls. And you'll also need a printer that accepts the roll paper adapter, such as the Epson Stylus Photo 870 and 1270. The Epson driver for these printers allows it to print right up to the edge of the roll paper. Manufacturers/Distributors |